Windows Server Managing and Supporting Active Directory Certificate Services(ADCS)
Cryptography
It is secure communication in the presence of third parties.
Goals of Cryptography
- Confidentiality - content is encrypted
- Data Integrity - content is not altered in transit
- Non-repudiation - sender of message cannot deny he did not send it at a later time
- Authentication - able to prove their ID to others
Encryption Methods
-
Symmetric Encryption - use same key to encrypt and decrypt, how to exchange key in a secure way would be a problem
eg: DES(Data Encryption Standard), 3DES, IDEA(International Data Encryption Algorithm), CAST, RC2,RC4,RC5,RC6, AES, Blowfish
-
Asymmetric Encryption (aka Public Key Encrpytion)
eg: RSA, DSA, ECC
-
Hybrid Cryptography - the encryption and decryption algoritm used in
real world- Asymmetric encryption is used to encrypt the shared key for symmetric encrpytion algorithm used to encryt the message
- symmetric encrpytion is used to encrypt message
Hash Functions & Digital Signatures
Hash is typically used to verify that a certain item has not been modified by providing a
digest(orfingerprint)
How hashing works
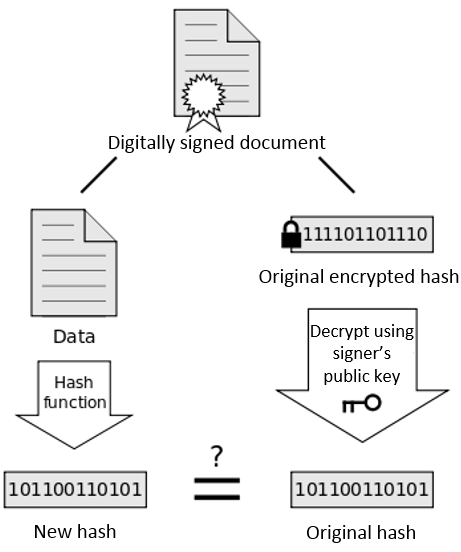
Characteristics of Digital Signatures
- Identification - the recipient can be sure of who send the message
- Integrity - recipient of a signed message can check it to make sure the message was not tampered
- Reliability/non-Repudiation - verify the sender truly sent the message with
digital signature
PKI
Digital Certificate
Digital credentials comparable to digital ID or digital passport.
Certificate Authorities (CA)
CA is a machine which issues corticates to different entities(users, computers, network devices etc)
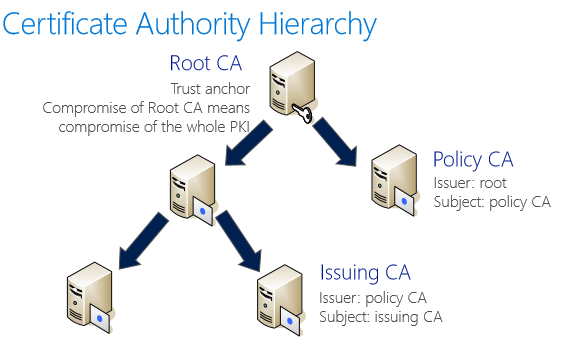
Reasons for hierarchies
- Security
- Mapping trust
- Manageability - role separation
- Flexibility - CA can be repleced easily for different levels of PKI
Certificate Revocation and Chain Building
Digital Certificate normally expires after 1 year. In some situation might cause a certifcate to be revoked before its expiration due to:
- Certificate is no longer used
- Details of certificate are changed
- The certificate owner’s private key was compromised
Certificate Revocation List (CRL)
Revocation Cache
Disk Cache
Maintains copies of all CRL and OCSP responses retrieved;
Items are maintained until their validity period expires;
Memory Cahce
Contains revocation information used by a specific process;
Maintained within the memory used by the calling process;
Online Certificate Status Protocol(OCSP)
Deploy a Two-Tier PKI Hierarchy
PKI Objects in AD
A PKI has no relationship to any AD, but when installing an AD integrated CA, AD will be used to store PKI related information that can be used by clients
related Information to AD Container
- AIA - Authority Information Access
- CDP - CRL Distrubution Points
- Certificate Templates
- Certification Authorities
- Enrollment Services
- KRA
- OID
- NTAuthCertificates
Certificate Stores
Logical containers, holding one or more certificates; logical view is comprised of the certificated from each of the physical certificate stores on the computer;
PKI Pre-Installation Tasks
- CA Administrator
Offline Root CA
- CA Auditing
- OS Auditing
- Publishing Root CA CRT and CRL Files
Subordinate Issuing CA
- Install and Configure Subordinate Issuing CA
Post-install Configuration
Powershell-based Installation of Subordinate Issuing CA
- Powershell 4.0 Deployment Cmdlets
- Powershell 4.0 Administration Cmdlets
Optional installation of CA Web Enrollment Proxy for FabrikamDevicesissuingCA01
Security
Exposure of CA Private Key
Private Key storage (Local Computer)
- On the CA’s hard drive
- In the CA computer’s memory
Private Key’s Risk Exposure
CA private key - the most important logical piece of data in PKI world
CA private key might fall into the wrong hands:
- physical hard disk can be stolen
- backups can be compromised
- virtualizd CA can be accessed by different people (Hyper-V admins, storage admins)
Stolen private key can be used to issue fraudulent certificates for unauthorized requestors
Hardware Security Modules
Private Key storage (HSM)
CA private key can be stored on an Hardware Security Module(HSM), implementing an HSM is the preferred option.
Features of HSM
- Hardware protection of valuable private keys
- Acceleration of cryptographic operations
- Enforce additional controls whenever the CA key is used (role separation, multiple eyes principle)
- Load balancing and failover in hardware modules using multiple HSMs linked together through a daisy chain
- Implementing an HSM is the answer to many (not all) security threats but adds cost and complexity to your environment
Risk Exposure due to CA Backup
Risk exposure if HSM is not implemented;
Mitigation factors for backups including CA private keys
Offline Certification Authorities
- an offline certification authorities means:
- truly offline, do not have a network interface
- are not joined to an Active Directory domain
- CRLs, certificate and cert requests have to be copied manually
- If physical - keep it in a safe place (eg separate rack)
- If virtual - remove from hypervisor and store 2 copies on encrypted storage devices
### Offline CAs and network HSM
If an offline CA is connected to a network based HSM:
- For virtual offline CA implementations, build a dedlicated VLAN between CA and the HSM
- For Physical offline CA implementations, establish a dedicated network connection to the HSM
- Use dedicate media to transfer data
- Update the OS with Service Packs and any updates that affect the logical operation of the CA
- Implement security Auditing
- use BitLocker or other full volume encrpytion method to encrypt hard disks
CA Hardening
Securing virtualized CAs
Protecting the CA Serivce
Role Separation
Common Criteria Roles
- CA Administrator
- Certificate Manager
- Backup Operator
- Auditor
Auditing
CA Auditing
OS Auditing
PKI Operations and Business Continuite
CA High Availability
- Semi redundant - 2 separate issuing CA with the same templates published
- Fully redundant - 1 issuing CA using Windows Failover Clustering
Offline CA Maintenance
- Offline CA CRL Publishing
Backup of PKI components
Backup Considerations
- Orphaned certificates
- Private key material presence
- Backup protection
CA private key and database
CA certificate Renewal
Validity period
- increases the certificate validity period
- Initial validity period is added to the date of the certificate renewal
- validity period for a self-signed certificate can be modified prior to renewal using the
%windir%\CAPolicy.inffile
[certsrv_server]
RenewalValidityPeriodUnits = 20
RenewalValidityPeriod = years
certificate renewal
- same key pair
- new key pair
CA Renewal and CRL Partitioning
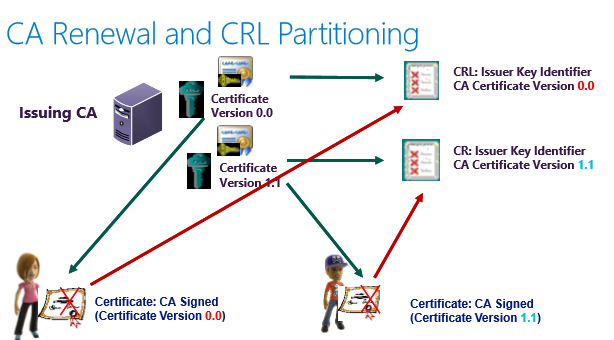
CA Renewal best practices
- Validity period of child CA should be no more than 50% of its parent
- Renewal of the CA certificate should be conducted at 50% of the validity period
CRL Maintenance
- Controlling CRL Size (size is increasing linear)
- Plan for partitioning after 100k enrolled
- plan for IDP (Issuing Distribution Point) 3rd party client support
Remove expried CRLs(if configured to be stored in the database)
Emergency Procedures
CRL Re-Signing/Emergency CRL Signing
Manually extending the validity time of a CRL
- CA Migration
- CA Recovery
- Disaster Recovery
Exit Modules
CA Monitoring
NDES - Advanced Enrollment Methods
NDES Overwiew: is a Microsoft implementation of Simple Certificate Enrollment Protocol (SCEP) used to enroll certificates to network devices
Allows switches/routers/smartphones.tablets to obtain certificates
Devices use NDES as proxy to get certificate from CA
Prerequisites
OCSP
Chain Building
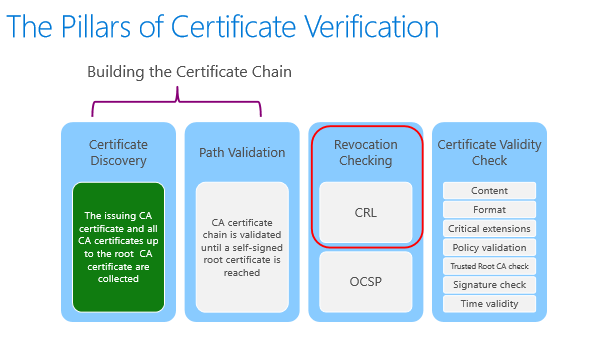
Base and Delta CRLs
Delta CRLs contains the list of revoked certificates since the last base CRL issurance
CRL Partitioning
CRL Overlap Period
- Back-dated by 10 minutes by default (clock skew)
CRL under the hood - Revocation reasons
- unspecified
- Key Compromise
- CA Compromise
- Change of Affiliation
- Superseded
- Cease of Operation
- Certificate Hold
- Remove from CRL
- Priviliege Withdrawn
- AA Compromise
OCSP Overview
In a nutshell:
- OCSP client searches for locally cached time-valid OCSP response from prior query
- OCSP client sends HTTP or HTTPS request to OSCP responder for certificate status providing the certificate serial # of interest
- OCSP responder reploes with a signed response that includes the revocation status of teh certifcate based on its cached knowledge from the CRL issued by the CA
- OCSP client validates the signature of the response prior to accepting and caching the response
- Valid response cached for remaining duration of OCSP responder cached CRL
OCSP Limitations
- Scalability limitations
Online service responding to a single certificate status requests results in higher load than CRL solution, requiring multiple and sometimes geographically dispersed servers to balance the load
-
The response signing and signature verification processes also takes time which can adversely affect the overall response time at the relying party
-
Finally, since the integrity of the signed resonse depends on the integrity of the OCSP responder’s signing key, the validity of the key is verified after a response is validated by the client.
OCSP Answers
GoodRevokedUnknown